Population-scale testing for COVID-19 is one of the best ways to limit mortality rates. Large-scale testing finds and isolates infections quickly, limiting the virus’ spread and protecting vulnerable populations. To properly survey populations, millions of COVID-19 test kits will need to be processed. Organizations around the world are trying to ramp their capacity as quickly as possible.
This is the type of challenge Opentrons was built to meet.
Opentrons’ COVID-19 Testing System is the best solution for labs running COVID-19 public health surveillance projects that need to immediately scale up to automated operations. Opentrons can install systems that automate up to 2,400 tests per day within days of an order being placed. We are currently deploying this surveillance capability at the Open Medicine Institute in Palo Alto, California, with more surveillance projects soon to follow.
We can work with any reagent provider, and even offer suggestions for the best and most affordable options. If you are a lab that needs to scale COVID-19 surveillance operations, please contact us at covid-19@opentrons.com.
Opentrons and the Open Medicine Institute are eager to work with local and federal agencies to determine if this system can be used for clinical diagnosis under Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) and provide testing bandwidth to meet the critically high and growing need.
Below are details about the system we’ve developed and how it can be deployed for COVID-19 testing at high-scale.
As with many infectious disease assays, the assay for detecting COVID-19 virus utilizes quantitative polymerase chain-reaction (qPCR) technology. In the case of a coronavirus like COVID-19, the assay is actually a reverse-transcriptase qPCR (RT-qPCR) because it measures RNA rather than DNA. The RT-qPCR is able to detect the presence and level of target COVID-19 sequences in RNA purified from the patient sample, which tells you if someone is infected and, if so, for approximately how long.
The first step is to collect samples. Collection happens after a doctor orders a test. Hospitals, labs, and public health facilities swab a patient’s nose or mouth and immediately place the test swab in a tube. Then these patient samples are safely brought to the testing lab.
Once the collection tubes get to the lab, there are three automated steps:

Each of these steps has a designated OT-2 workstation (with the exception of the assay, which happens on a qPCR instrument that the lab provides). Here is how to automate the process on Opentrons:

Station A – Sample Plating: 96 collection tubes with patient samples suspended in deactivation buffer are put on the first Opentrons robot to be reformatted for RNA extraction. The robot pipettes samples and positive controls from tubes into the deep-well plate.
Station A Configuration: $9,050

Station A should be in some type of “intake” room. The main bottleneck on this station is often not the actual reformatting but labeling, logging, uncapping, and loading collection tubes into racks for the robot. It is best to keep the sample intake room separate from any space where sample processing happens in order to prevent contamination. Once samples and positive control RNA are put into the deep well plate, it can be moved to Station B.

Station B – RNA Extraction: 96 deep-well plates containing samples are moved to the second robot for RNA extraction using magnetic microbeads. This is the bulk of the automated process due to the many wash steps required to fully purify the RNA.
Station B Configuration: $7,750

There should also be a dedicated extraction room where all the Station B extraction robots are housed. If throughput demands it, this room can also house a reagent filling station to prepare the magnetic micro-beads and buffers for Station B robots to run RNA extractions. As you can see in the deckmap above, there are a lot of reagents and tips required for this process.

Station C – Assay Setup: The RNA isolated from the samples (elution) is then moved to a third room that houses the qPCR instrument and is designed to be as “clean” as possible to minimize contamination. The plate with pure sample RNA is placed onto an Opentrons robot to be prepped for the RT-qPCR assay.
Station C OT-2 Configuration: $7,500

The reagents required for the RT-qPCR are placed individually onto the Temperature Module for active cooling. These are combined into a mastermix, which is then distributed into a plate and combined with purified RNA. After this process, the plate is ready to be put into the qPCR machine and analyzed for the presence of COVID-19.
We’ve developed a system of 8 robots (2x Station A, 4x Station B, 2x Station C) that can automate the preparation of 12 96-well plates every 12hrs, or approx 2,400 tests / day.

This is how the timing of the process breaks down with the 8 robot system:

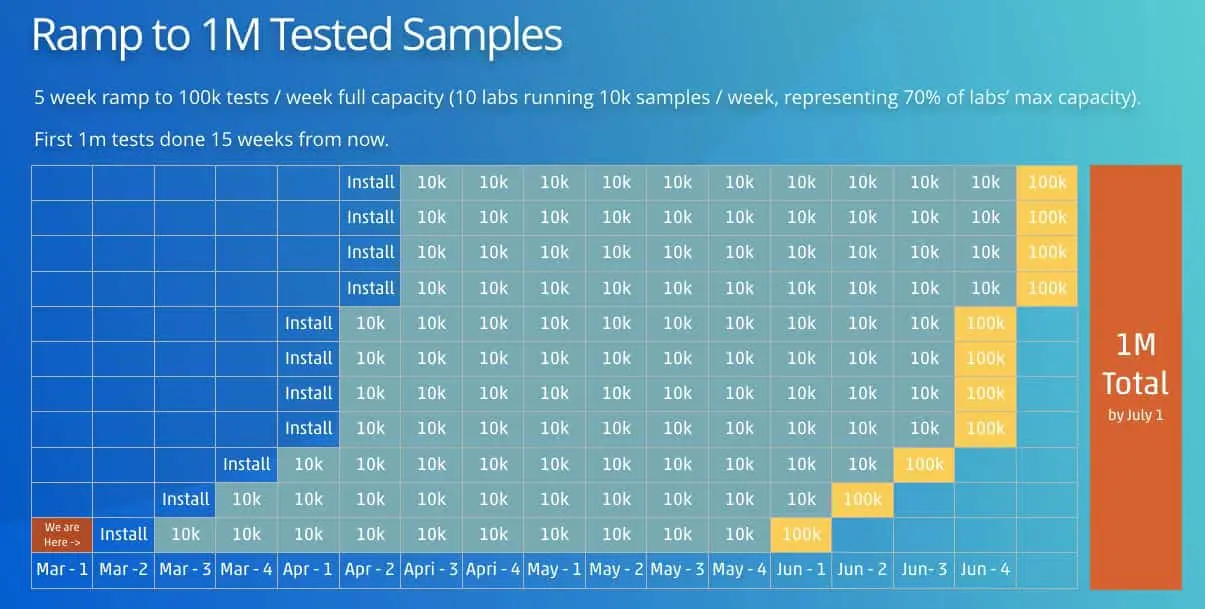
This system plus spare parts and in-lab installation is available for $100,000 for surveillance projects. We can ramp the installation of these systems at 1x installation per week through March, and then 4x system installations per week in April. If we achieve this ramp, we can expect to automate 1M tests on the Opentrons system by the end of June.

We are currently working to install the first high-throughput system at the Open Medicine Institute in Palo Alto, California, and are eager to use our robots to aid labs in completing this critical project.
If you are interested in working with Opentrons to scale your lab’s ability to run COVID-19 testing, please contact [email protected].